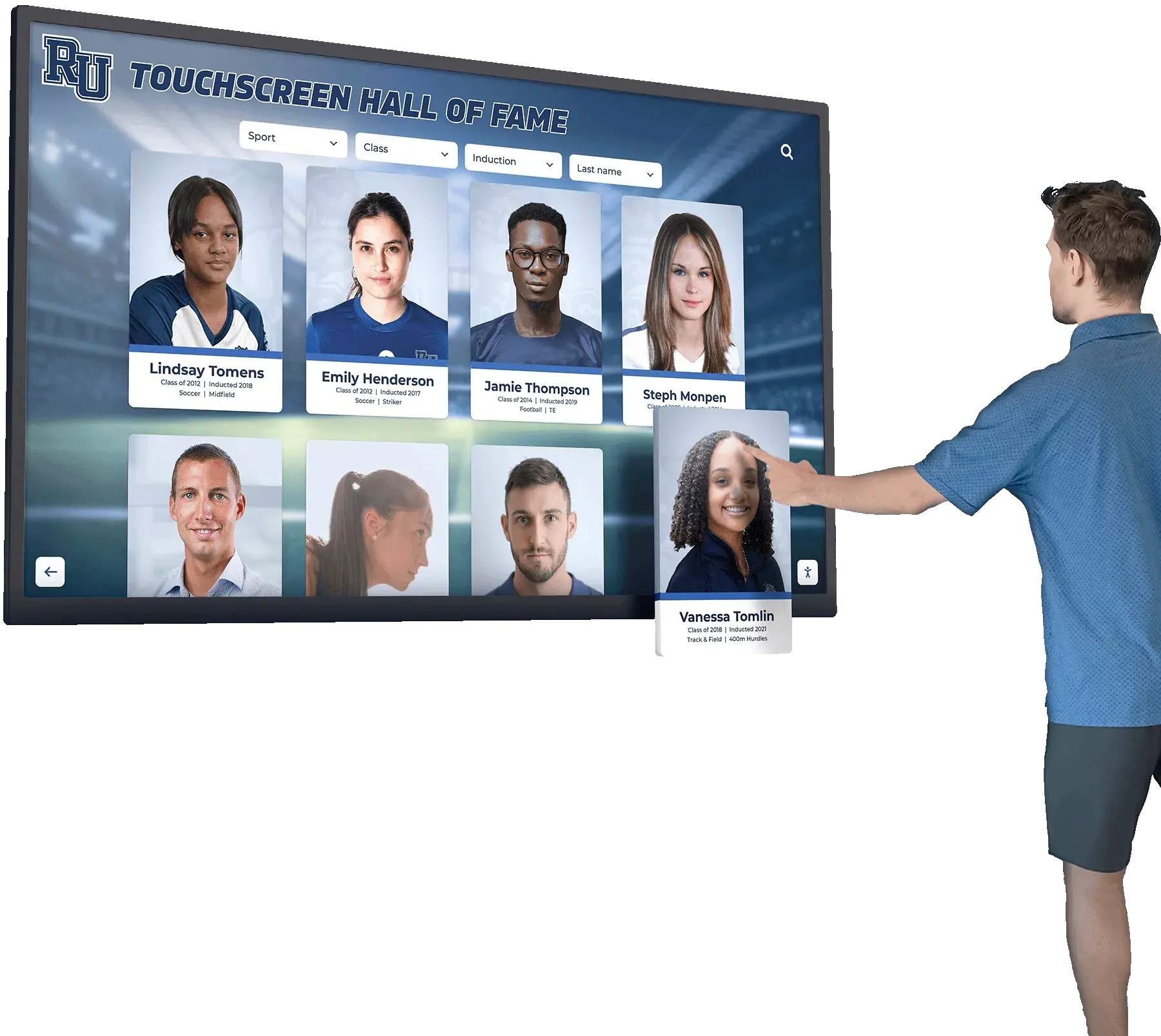
The question “is marching band a sport?” sparks passionate debate in school hallways, online forums, and athletic director offices across the nation. Marching band students dedicate countless hours to rigorous physical training, master complex choreography while performing intricate musical arrangements, and compete in high-stakes competitions—yet many schools still categorize band as an extracurricular activity rather than an athletic pursuit. This classification gap creates real consequences: unequal recognition, limited access to athletic facilities, and invisible achievements that rarely receive celebration matching the effort invested.
Meanwhile, marching band members demonstrate cardiovascular endurance rivaling cross-country runners, carry instruments weighing 30-40 pounds while executing precision formations, and perform under competitive pressure that would challenge any athlete. They rehearse through summer heat, perfect routines requiring thousands of repetitions, and represent their schools at competitions judged with the same rigor as athletic contests. Yet trophy cases overflow with football memorabilia while band achievements occupy forgotten corners, if they appear at all.
This comprehensive guide examines the sport versus activity debate from multiple perspectives—definitional, physical, competitive, and cultural—while providing practical frameworks for ensuring marching band programs receive recognition commensurate with their dedication, skill development, and contribution to school pride regardless of classification labels.
The marching band recognition gap extends beyond philosophical debates—it affects student motivation, program funding, facility access, and community perception. Schools that approach recognition systematically create inclusive environments celebrating excellence across all competitive domains while building comprehensive school pride that honors diverse achievement pathways.

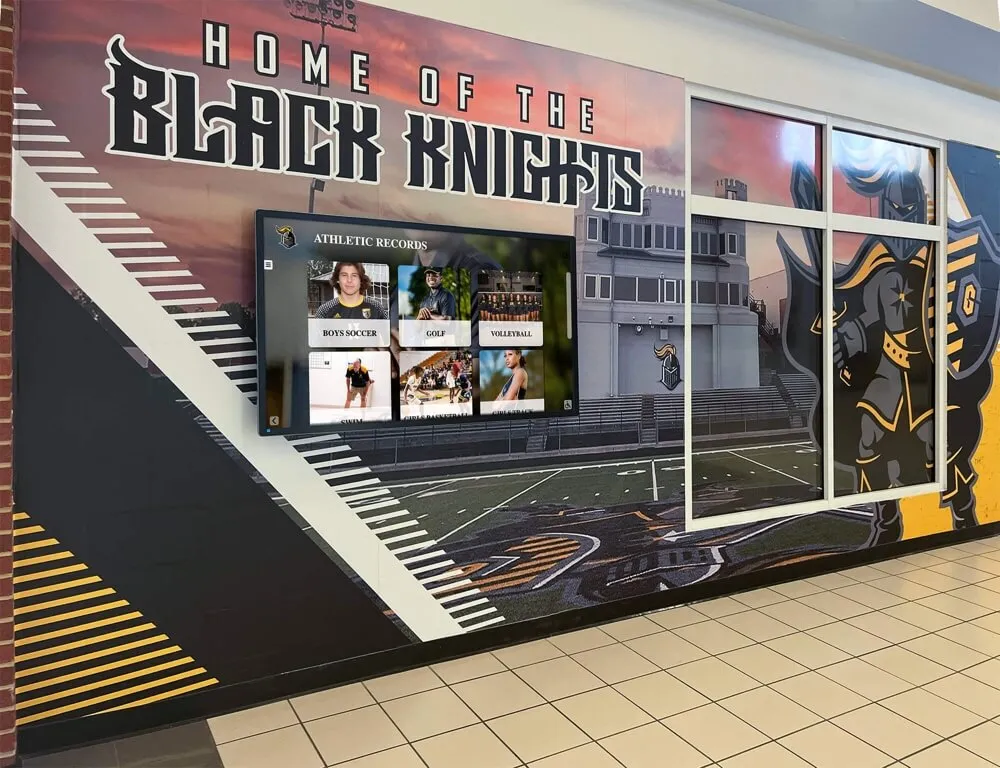
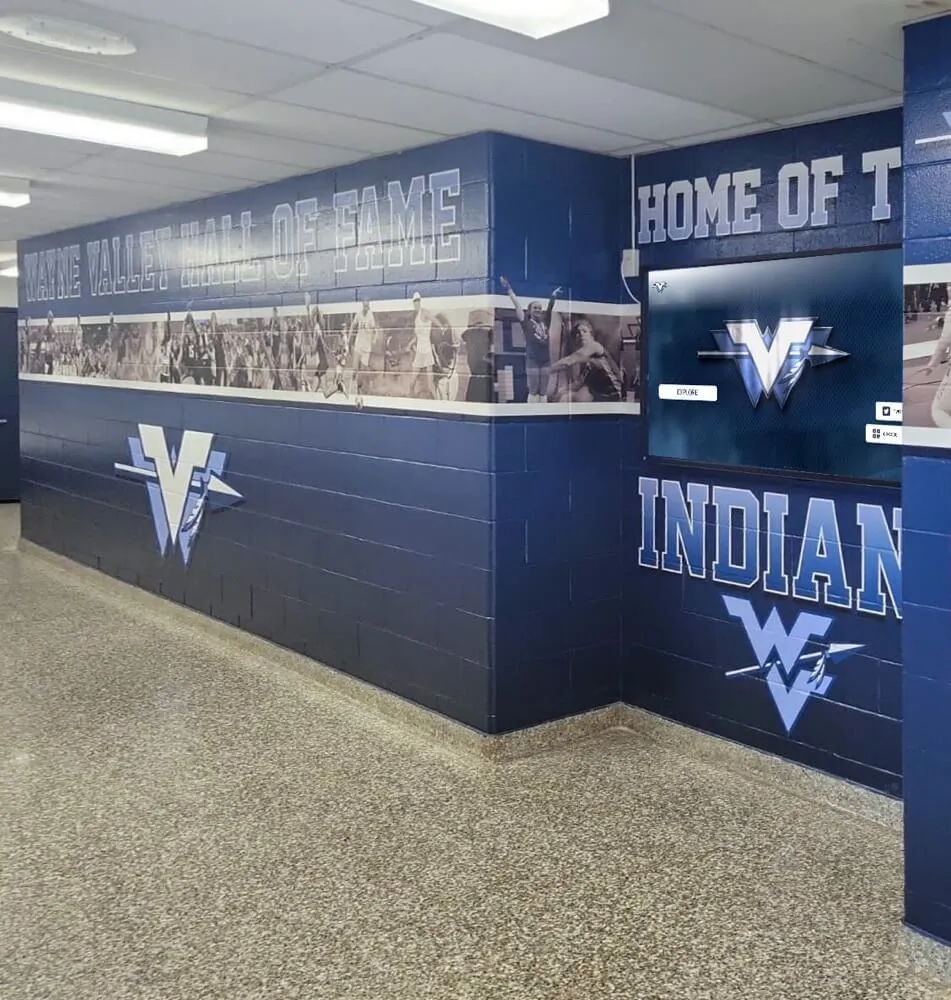
Modern schools recognize diverse achievements including marching band excellence through comprehensive display systems
Understanding the Sport Definition Debate
Before establishing recognition frameworks, understanding the definitional landscape helps administrators navigate classification discussions thoughtfully while focusing on practical recognition outcomes.
Traditional Sport Definition Criteria
Dictionary definitions and athletic organizations typically define sports through several core characteristics:
Physical Exertion and Skill Requirements
Traditional sport definitions emphasize:
- Sustained physical activity requiring cardiovascular fitness and muscular endurance
- Developed physical skills through systematic training and practice
- Coordination demands integrating multiple body systems simultaneously
- Strength and flexibility requirements essential for performance execution
- Injury risk from physical demands and performance conditions
Marching band demonstrably meets these criteria—members march miles during rehearsals and performances, carry heavy instruments while maintaining precise formations, and develop specialized motor skills through hundreds of practice hours.
Competitive Structure and Scoring Systems
Sport classification often requires:
- Organized competition against other participants or teams
- Objective scoring systems or judging frameworks determining winners
- Seasonal structure with progressive skill development
- Championship events determining elite performers
- Rankings comparing performance across multiple competitions
Marching band competitions feature elaborate judging systems evaluating musical performance, visual execution, general effect, and overall achievement—producing scored rankings as objective as any athletic scoreboard.
Governing Bodies and Standardized Rules
Recognized sports typically include:
- National or regional governing organizations establishing standards
- Codified rules creating consistent competition frameworks
- Safety regulations protecting participant wellbeing
- Equipment specifications ensuring fair competition
- Training and certification for officials and judges
Organizations like Bands of America (BOA), Winter Guard International (WGI), and state marching band associations provide exactly these governance structures—parallel to those overseeing traditional athletic competitions.

Recognition systems should celebrate achievement across athletic and artistic competitive domains equally
The Physical Demands of Marching Band Performance
Quantifiable data reveals marching band’s substantial athletic requirements that match or exceed many recognized sports.
Cardiovascular and Endurance Requirements
Research documenting marching band physical demands demonstrates significant athletic effort:
A study by the American College of Sports Medicine found that marching band members’ heart rates during performances averaged 145-160 beats per minute—comparable to moderate-intensity running. During full rehearsals and performances, members frequently maintain elevated heart rates for extended periods exceeding typical athletic practice durations.
Marching band shows typically span 8-12 minutes of continuous physical activity while simultaneously executing complex musical and visual elements—a multitasking challenge without parallel in most traditional sports where athletes focus on single performance domains.
Strength and Coordination Demands
The physical requirements extend beyond cardiovascular fitness:
- Instrument Weight: Sousaphones weigh 25-35 pounds, bass drums 20-30 pounds, with performers supporting this weight while marching and playing for hours during rehearsals
- Carrying Position: Many instruments require sustained arm elevation or asymmetric body positioning creating muscular demands
- Marching Technique: High-step marching with proper posture requires significant leg strength and core stability
- Precision Coordination: Executing drill formations at speeds reaching 180+ steps per minute while playing instruments demands exceptional motor control
- Environmental Challenges: Summer rehearsals in full uniform under extreme heat conditions test endurance like two-a-day football practices
Programs can explore comprehensive approaches to recognizing these physical achievements through academic and extracurricular recognition frameworks that celebrate diverse excellence.
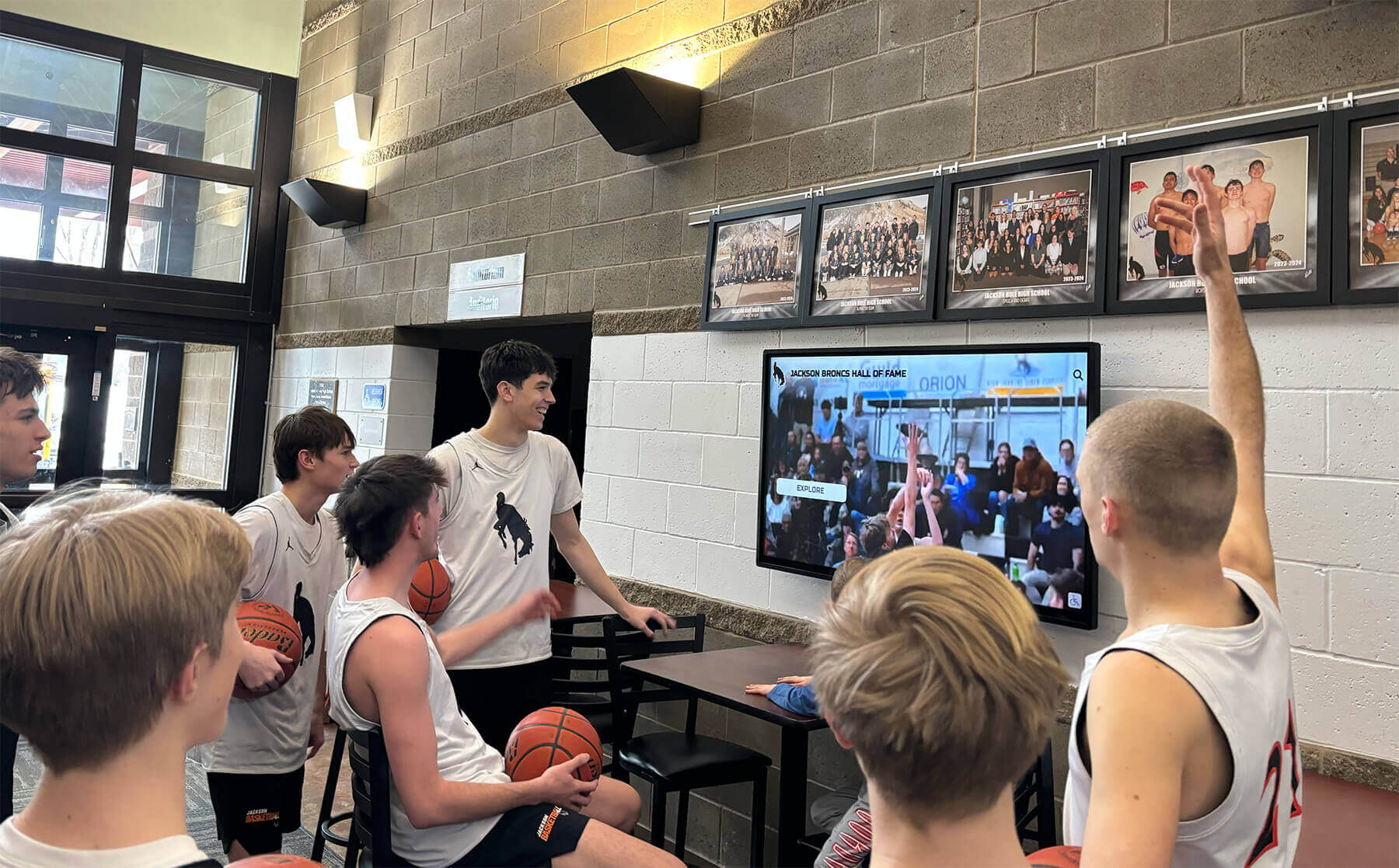

Interactive displays enable students to explore achievement stories across athletic and performing arts programs
Injury Rates and Physical Risks
Marching band participation carries genuine injury risks comparable to many athletic pursuits:
- Repetitive stress injuries from instrument playing positions and marching technique
- Heat-related illness during summer rehearsals and outdoor performances
- Acute injuries from collisions during formation transitions or equipment handling
- Overuse injuries affecting shoulders, backs, and lower extremities
- Dehydration and fatigue-related incidents during extended rehearsals
Medical research published in sports medicine journals documents these injury patterns, with some studies finding marching band injury rates approaching those of certain recognized sports when adjusted for participation hours.
Program Snapshot: Marching Band Achievement Recognition Framework
| Program Element | Details |
|---|---|
| Recognition Categories | Competition placements, individual section awards, leadership roles, years of participation |
| Display Integration | Lobby or performing arts center locations with equal prominence to athletic displays |
| Competitive Season | Summer rehearsals through fall competition season (July-November typically) |
| Achievement Tracking | Competition scores, rankings, special recognitions, festival ratings |
| Individual Honors | Section leaders, drum majors, soloists, state band selections |
| Documentation Methods | Performance videos, competition programs, score sheets, photographs |
| Update Frequency | Post-competition updates throughout season, comprehensive annual updates |
| Budget Considerations | Initial display investment plus ongoing content updates and maintenance |
The Case for Marching Band as a Sport
Multiple compelling arguments support classifying marching band within athletic frameworks based on objective criteria rather than traditional categorizations.
Meeting Objective Sport Criteria
When evaluated against standard sport definitions, marching band satisfies most or all requirements:
Physical Activity Component: Marching band members engage in sustained physical exertion throughout rehearsals and performances, meeting cardiovascular activity thresholds defining moderate to vigorous exercise.
Competitive Framework: Organized competitions with scoring systems, rankings, and championship events mirror athletic competition structures exactly.
Skill Development Through Training: Members undergo systematic training developing specialized skills through deliberate practice—identical to athletic skill development processes.
Team Coordination Requirements: Successful performances demand synchronized team execution where individual errors affect overall outcomes—the essence of team sport participation.
Seasonal Structure: Defined competitive seasons with progressive skill building, regular practice schedules, and culminating championship events parallel traditional sports calendars.
Schools establishing comprehensive recognition systems can reference building school pride through inclusive achievement celebration strategies that honor diverse excellence.
Comparative Athletic Demands
Examining marching band demands alongside recognized sports reveals comparable or exceeding physical requirements:
Practice Time Investment: Competitive marching bands rehearse 15-25 hours weekly during season—matching or exceeding most high school athletic practice schedules. Summer band camps involve full-day rehearsals for weeks, similar to two-a-day athletic training camps.
Performance Duration: An 8-10 minute marching band show represents continuous high-intensity physical and cognitive activity. By contrast, basketball players typically play 16-24 minutes during games with frequent substitutions, and football players execute plays lasting 5-10 seconds with 30-second rest intervals between plays.
Multitasking Complexity: Marching band members simultaneously execute precise marching formations, perform complex musical passages, maintain proper playing technique, express appropriate emotional interpretation, and respond to changing conditions—a cognitive load exceeding most athletic activities where physical execution predominates.
Year-Round Commitment: Successful programs extend beyond fall competition season, incorporating winter guard, indoor percussion ensembles, spring training, and summer rehearsals—creating year-round participation mirroring elite athletic training schedules.
Recognition Equity Arguments
Beyond definitional debates, equity considerations support equal recognition regardless of classification:
Equal Dedication Deserves Equal Recognition: Students investing comparable time, effort, and dedication deserve recognition matching their commitment level regardless of activity classification.
Program Value to School Identity: Marching bands represent schools at competitions, community events, and performances—contributing to institutional reputation and pride alongside athletic teams.
Inclusive School Culture: Recognition systems celebrating diverse achievement pathways create more inclusive environments where varied student talents receive appropriate honor.
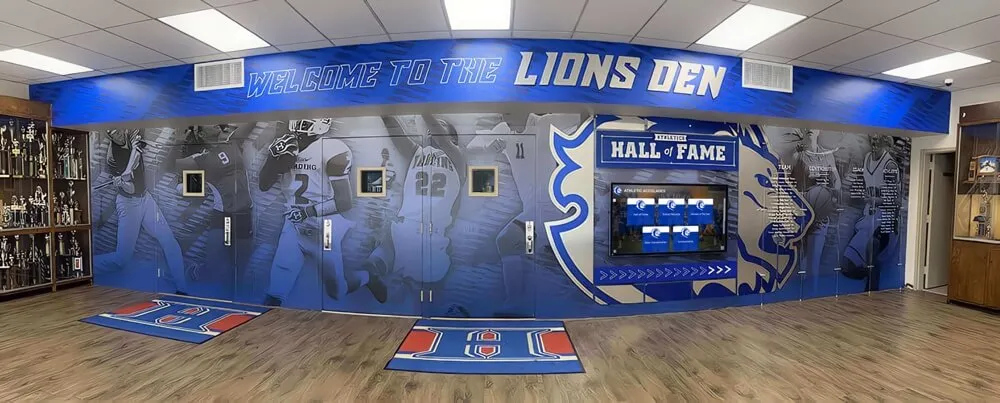

Comprehensive recognition displays celebrate achievement across all competitive domains including performing arts
College Recruitment Parallels: Competitive marching band participation enhances college applications and can lead to scholarships—functioning similarly to athletic recruitment processes.
Community Support and Engagement: Marching band performances draw substantial community audiences and generate school spirit comparable to athletic events, warranting equivalent visibility in recognition displays.
The Case Against Marching Band Sport Classification
Understanding opposing perspectives helps administrators navigate classification discussions while focusing on practical recognition outcomes regardless of definitional conclusions.
Artistic Performance Component
Primary arguments against sport classification emphasize performing arts elements:
Subjective Judging Standards: Unlike sports with objective scoring (basketball points, race times), marching band judging incorporates subjective artistic evaluation—interpreting musical expression, visual effect, and overall program conception. This subjectivity aligns more closely with fine arts competitions (theater, dance, visual arts) than objective athletic scoring.
Primary Purpose as Performance Art: Marching band’s fundamental purpose involves musical and visual artistic expression rather than physical competition. The physical demands serve artistic goals rather than representing intrinsic competition objectives.
Aesthetic Evaluation Criteria: Judges assess aesthetic qualities—musical tone quality, expressive interpretation, visual design sophistication—that transcend physical execution to encompass artistic merit.
Creative and Interpretive Elements: Programs involve creative design, thematic interpretation, and artistic vision more aligned with performing arts productions than athletic competitions.
Traditional Categorical Distinctions
Historical classification frameworks create institutional separation between athletics and performing arts:
Organizational Structure: Most schools administratively separate athletic departments from performing arts programs, with different leadership, budgets, and facility allocations reflecting distinct categorical treatment.
Participation Motivations: Students typically join marching band for musical and social experiences rather than competitive athletic aspirations, suggesting participant perception aligns with performing arts rather than athletic frameworks.
Educational Standards: State education codes typically classify band within fine arts graduation requirements rather than physical education or athletic credits, reflecting systemic categorical distinctions.
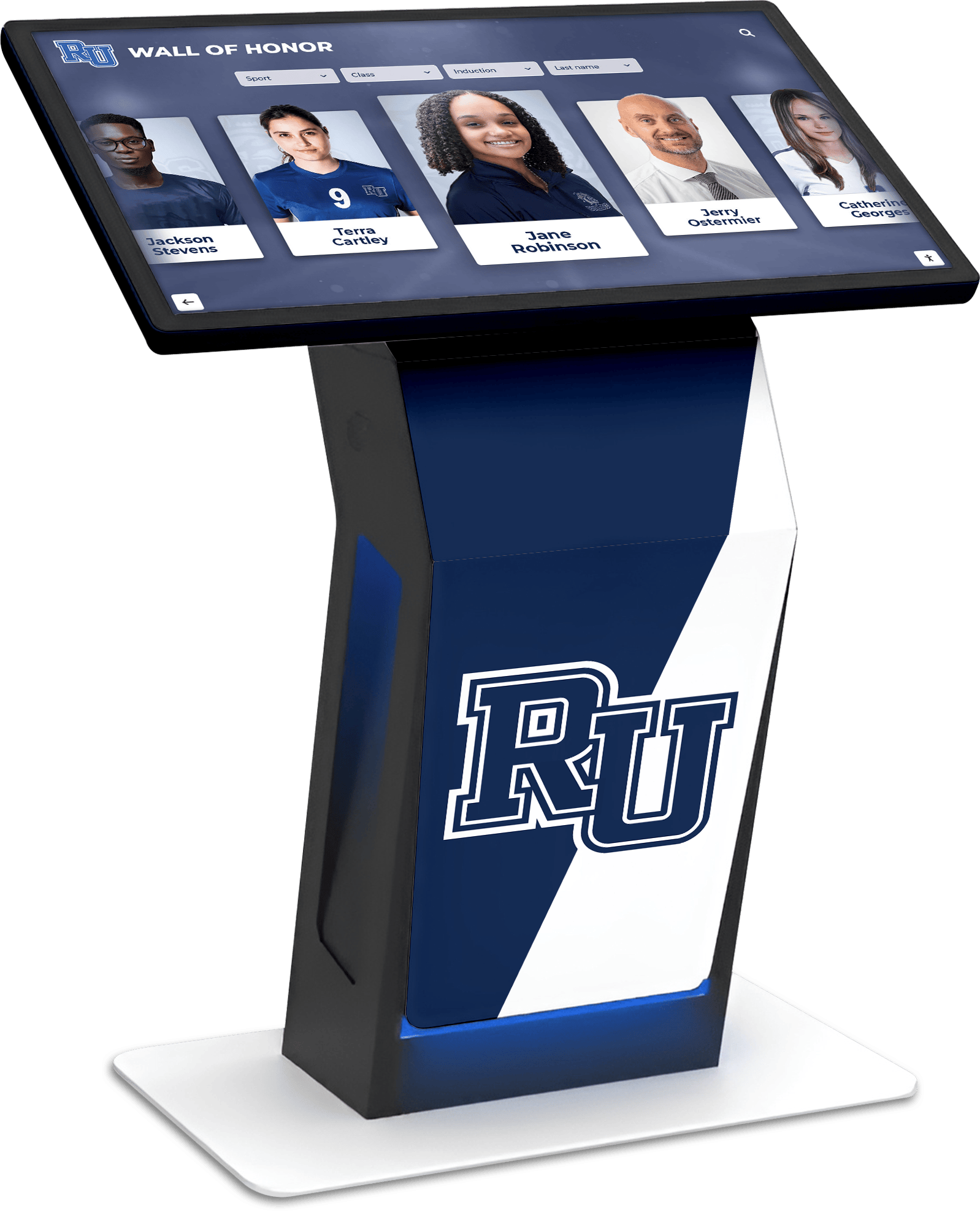

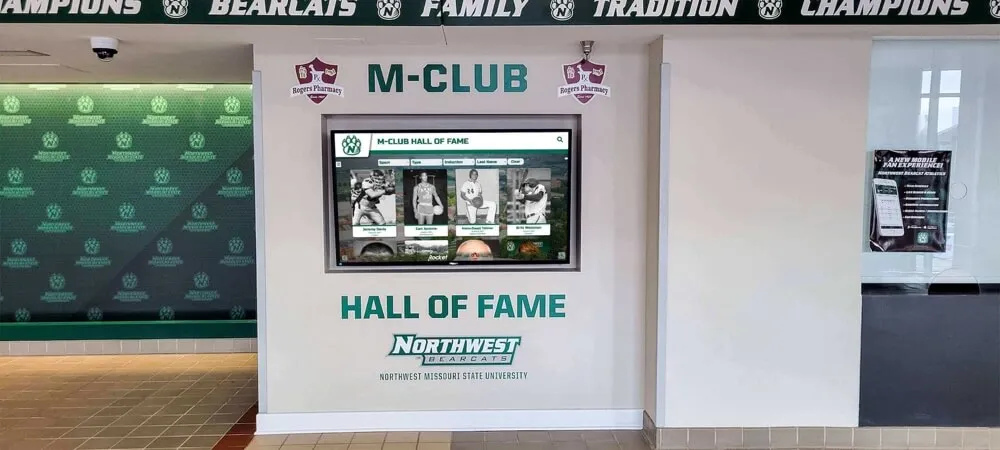
Modern recognition systems accommodate diverse achievement types through flexible display frameworks
Hybrid Classification Considerations
Many administrators and educators advocate hybrid perspectives acknowledging both athletic and artistic dimensions:
Sport-Art Fusion: Marching band represents unique fusion domains combining athletic physical demands with artistic performance elements—potentially warranting distinct classification beyond binary sport/non-sport categories.
Activity-Specific Classification: Rather than forcing universal categorization, schools might evaluate specific marching band components independently—recognizing competitive aspects as sport-like while honoring artistic elements as performance art.
Functional Recognition Over Definitional Debates: Perhaps definitional classification matters less than ensuring functional outcomes—equitable facility access, appropriate recognition, adequate funding, and cultural respect—regardless of categorical labels applied.
Schools implementing recognition programs can explore digital signage content strategies that celebrate achievements across categorical boundaries.
Building Comprehensive Recognition Systems for Marching Band Excellence
Beyond definitional debates, practical recognition frameworks ensure marching band achievements receive appropriate celebration regardless of sport classification conclusions.
Multi-Dimensional Achievement Tracking
Comprehensive recognition systems document diverse accomplishment categories reflecting marching band’s multifaceted excellence:
Competitive Performance Recognition
Track and display competition results demonstrating objective achievement:
- Competition placements and rankings at invitational tournaments
- State championship results and finals advancement
- Regional and national competition participation and results
- Year-over-year performance improvement trends
- Head-to-head comparisons against traditional rival programs
- Superior and excellent ratings at festival evaluations
Individual Excellence Honors
Recognize personal achievements contributing to collective success:
- Drum major selections and leadership roles
- Section leader appointments across instrumental groups
- All-state band selections from marching program members
- Solo and ensemble competition achievements
- Outstanding performer awards at competitions
- Years of participation and dedication milestones
Program Development Recognition
Celebrate growth and program quality indicators:
- Enrollment growth reflecting program appeal and retention
- Equipment upgrades and facility improvements
- Competition advancement from lower to higher classification levels
- Expansion of associated programs (winter guard, indoor percussion)
- Community performances and civic engagement appearances
- Educational outcomes including college music program placements
Programs developing recognition content can reference end-of-year awards frameworks applicable to band achievements.

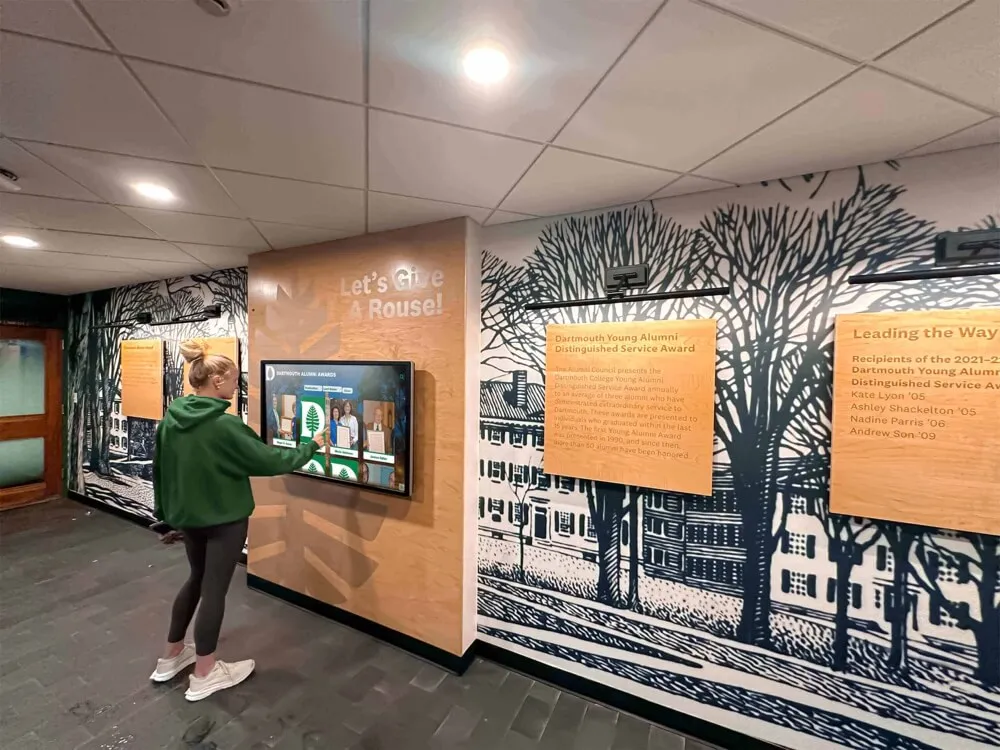
Touchscreen recognition systems enable detailed exploration of individual and group achievements
Display Integration and Visibility
Physical recognition placement significantly impacts program perception and student motivation:
Location Strategies for Equal Visibility
Recognition placement should reflect achievement value rather than categorical distinctions:
- Main entrance areas: Position band recognition displays in primary school entry points alongside athletic displays
- Performing arts center lobbies: Create comprehensive display systems in performance venues celebrating musical excellence
- Shared athletic-arts corridors: Develop integrated recognition hallways honoring diverse achievement forms
- Competition trophy displays: Provide trophy case space for band competition hardware equivalent to athletic trophy prominence
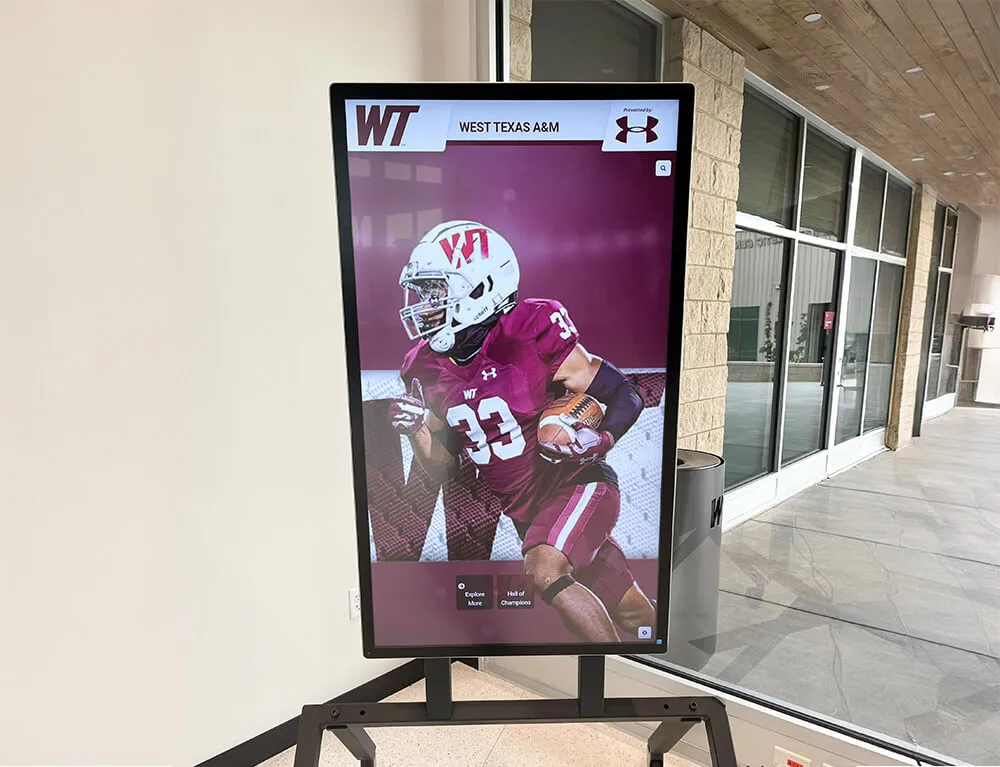
- Digital display integration: Incorporate marching band content into lobby digital signage rotations equally with athletic highlights
Content Presentation Approaches
Effective displays communicate achievement significance through comprehensive storytelling:
- Competition score sheets and judge commentary demonstrating objective evaluation
- Performance videos capturing show complexity and execution quality
- Behind-the-scenes rehearsal documentation showing preparation intensity
- Individual member profiles highlighting personal dedication and achievement
- Timeline presentations showing program development and success trajectory
- Comparative data positioning band achievements within broader competitive contexts
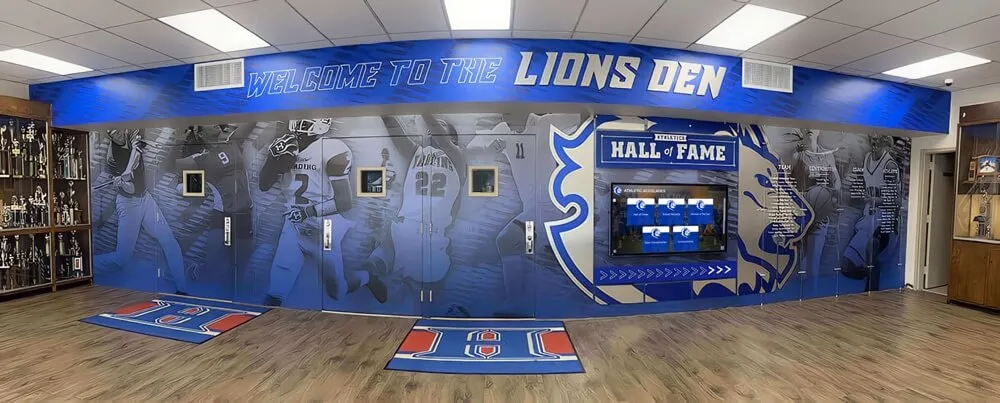
Schools planning comprehensive recognition displays can explore athletic hall of fame frameworks adapted for band program recognition.
Digital Recognition Solutions for Comprehensive Band Honor
Modern technology enables recognition systems that overcome physical space limitations while providing comprehensive achievement documentation:
Touchscreen Display Advantages
Interactive digital displays offer unique benefits for marching band recognition:
- Unlimited capacity: Digital systems accommodate growing achievement records without physical space constraints limiting traditional plaques
- Rich multimedia integration: Display performance videos, audio clips, and photo galleries impossible with static displays
- Dynamic content updates: Easily update displays throughout competitive season reflecting current achievements
- Detailed individual profiles: Provide comprehensive member biographies, achievement lists, and personal stories
- Historical program timeline: Document complete program history showing development across decades
- Competition comparison data: Present scoring data and competitive context unavailable in traditional recognition formats
Content Architecture for Band Recognition Displays
Comprehensive digital displays typically incorporate several content modules:
- Current season highlights: Real-time updates showing recent competition results and performance highlights
- Historical achievement archive: Complete program records documenting excellence across all years
- Individual member galleries: Searchable databases of all participants with achievement profiles
- Video performance library: Archived competition performances and special event appearances
- Photo galleries: Extensive image collections from rehearsals, competitions, and performances
- Leadership recognition: Dedicated sections honoring drum majors, section leaders, and program directors
- Competition result databases: Comprehensive scoring records showing performance trends and comparative rankings
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide digital recognition displays specifically designed to celebrate diverse student achievements including marching band excellence, offering unlimited capacity for documenting program success and individual contributions while maintaining equal visual prominence with athletic recognition systems.
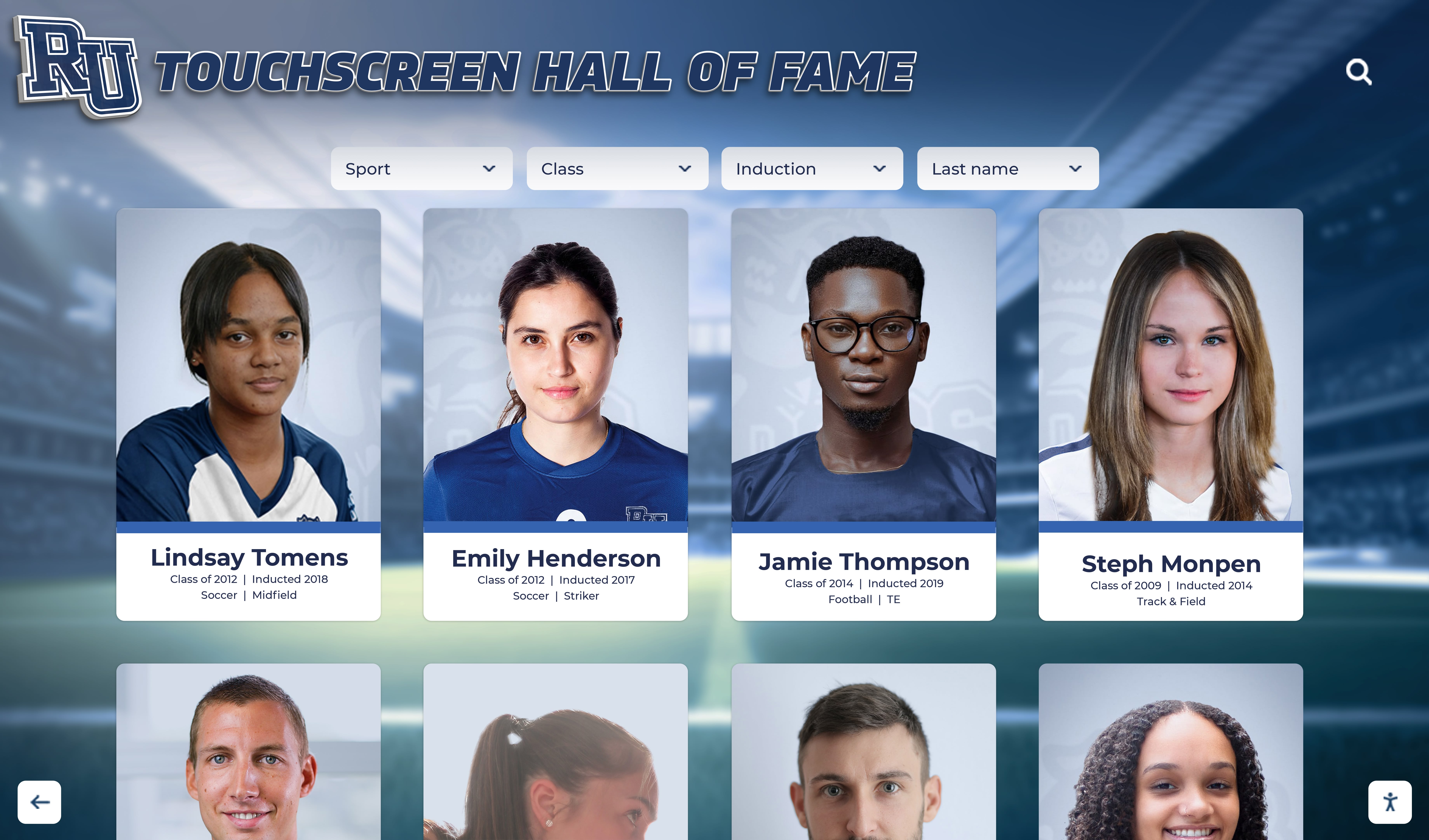
Digital systems enable detailed achievement profiles impossible with traditional static recognition approaches
Creating Recognition Programs That Transcend Classification Debates
Rather than allowing definitional debates to impede recognition, effective programs focus on functional equity ensuring appropriate honor regardless of categorical labels.
Recognition Equity Principles
Foundational principles guide equitable recognition across all achievement domains:
Achievement-Based Recognition Standards: Establish recognition criteria based on dedication, skill development, competitive success, and program contribution rather than activity classification. If criteria warrant athletic recognition, band achievements meeting identical standards deserve equivalent honor.
Visibility Parity Commitments: Ensure band recognition receives physical prominence, display space, and community visibility matching athletic recognition. Position displays in equivalent locations and allocate comparable resources.
Resource Allocation Equity: Provide recognition program budgets proportional to participation levels and achievement significance rather than traditional categorical funding disparities.
Celebration Inclusion: Incorporate band achievements into schoolwide recognition events, ceremonies, and communications with equal emphasis as athletic accomplishments.
Student Voice Integration: Include band members in discussions about recognition approaches, ensuring solutions reflect participant values and program culture.
Facility Access and Support Systems
Recognition extends beyond display systems to encompass comprehensive program support:
Practice Facility Equity: Ensure marching band programs receive appropriate rehearsal facilities including fields, indoor spaces, and equipment storage comparable to athletic program provisions.
Academic Support Services: Provide academic support for band students managing demanding rehearsal schedules similar to athletic academic support programs.
Transportation and Equipment: Fund travel to competitions and equipment purchases with considerations parallel to athletic program support.
Medical and Training Support: Offer access to athletic training services, hydration resources, and injury prevention programs reflecting marching band’s physical demands.
Programs developing comprehensive student support can reference youth sports recognition frameworks applicable to band program structures.
Measurement and Continuous Improvement
Systematic evaluation ensures recognition programs achieve intended equity outcomes:
Recognition Audits: Periodically assess physical display space, digital content allocation, communication mentions, and resource distribution across athletic and band programs, identifying equity gaps.
Stakeholder Feedback: Regularly survey band students, families, and alumni regarding perceived recognition adequacy and program support.
Participation Impact Analysis: Monitor enrollment trends and retention rates correlating with recognition program enhancements.
Community Perception Research: Assess community understanding of band program achievements and whether recognition effectively communicates program excellence.
Achievement Outcome Tracking: Document recognition program impacts on student motivation, program quality, and competitive success.
Addressing Common Concerns and Implementation Challenges
Schools transitioning toward recognition equity often encounter predictable challenges requiring thoughtful navigation.
Budget and Resource Constraints
Challenge: Limited resources create competition for recognition funding between athletic and band programs, with administrators concerned that enhanced band recognition reduces athletic recognition budgets.
Resolution Approaches:
- Frame recognition investments as additive rather than competitive—expanding total recognition capacity rather than redistributing existing resources
- Pursue band booster fundraising specifically for recognition displays, reducing general fund requirements
- Implement phased recognition enhancements spreading costs across multiple budget cycles
- Leverage digital recognition solutions that provide greater capacity per dollar invested compared to traditional physical displays
- Explore partnership opportunities with local businesses supporting performing arts programming
Tradition and Cultural Resistance
Challenge: Established recognition traditions prioritizing athletics create cultural inertia and stakeholder resistance to recognition program changes.
Resolution Approaches:
- Emphasize recognition expansion rather than reduction—adding band recognition without diminishing athletic honor
- Engage alumni band members in recognition planning, creating advocacy constituencies supporting program changes
- Document other schools’ successful integrated recognition programs providing implementation models
- Frame changes around comprehensive school pride that celebrates all excellence forms
- Start with smaller recognition pilots demonstrating value before pursuing comprehensive programs

Comprehensive recognition programs celebrate school identity across all competitive and achievement domains
Definitional Classification Debates
Challenge: Stakeholders insist on resolving sport classification questions before implementing recognition changes, creating analysis paralysis.
Resolution Approaches:
- Redirect focus from definitional debates toward functional equity outcomes—appropriate recognition regardless of classification
- Acknowledge legitimate perspectives on both sides of classification debate while maintaining that recognition shouldn’t depend on definitional resolution
- Frame recognition around achievement, dedication, and school contribution rather than categorical membership
- Create recognition systems flexible enough to honor athletic, artistic, and hybrid achievement forms without forcing classifications
- Focus administrative decisions on practical student experience rather than abstract definitional questions
Implementation Timeline: Launching Comprehensive Band Recognition
Schools implementing enhanced band recognition benefit from systematic rollout approaches balancing ambition with practical constraints.
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning (Months 1-3)
Recognition Audit: Document current band recognition systems including display locations, content, visibility, and resources. Compare systematically with athletic recognition programs identifying specific equity gaps.
Stakeholder Engagement: Convene planning committees including band directors, students, parents, alumni, administrators, and community members. Gather input on recognition priorities, preferred approaches, and implementation concerns.
Budget Development: Establish recognition enhancement budgets through combinations of general funds, booster fundraising, grants, and donor cultivation targeting band recognition improvements.
Solution Research: Investigate recognition approaches including traditional plaques, trophy cases, wall murals, and digital displays. Evaluate options based on capacity, cost, maintenance, and long-term flexibility.
Phase 2: Design and Content Development (Months 4-6)
Recognition Content Assembly: Gather comprehensive achievement data including competition results, individual honors, historical program information, photos, videos, and biographical content for recognition displays.
Display Design: Develop display layouts and designs ensuring professional quality, appropriate prominence, and brand consistency with overall school identity while celebrating band program uniqueness.
Technology Selection: If pursuing digital recognition, evaluate software platforms, hardware options, installation requirements, and ongoing management needs. Prioritize solutions offering easy content updates and unlimited expansion capacity.
Schools evaluating digital recognition can explore interactive touchscreen solutions for museums and schools applicable to band recognition displays.
Phase 3: Installation and Launch (Months 7-9)
Physical Installation: Complete display installation including construction, technology setup, content loading, and finishing details ensuring professional-quality results.
Content Population: Load comprehensive achievement content including historical records, current season information, individual profiles, media galleries, and supporting documentation.
Testing and Refinement: Conduct thorough testing ensuring all display elements function correctly, content displays properly, and user interactions work intuitively.
Launch Event: Plan recognition display unveiling as community event celebrating band program excellence while demonstrating institutional commitment to comprehensive achievement recognition.
Phase 4: Ongoing Management (Months 10+)
Regular Content Updates: Establish systems for ongoing content updates throughout competitive season reflecting current achievements and maintaining display relevance.
Performance Monitoring: Track display engagement, stakeholder feedback, and program outcomes assessing recognition system effectiveness.
Continuous Enhancement: Regularly expand content, refine presentations, and incorporate new features maintaining display quality and relevance across years.
Conclusion: Moving Beyond Debate to Comprehensive Recognition
The question “is marching band a sport?” generates passionate arguments reflecting genuine uncertainty about activity classification and appropriate recognition frameworks. Marching band demonstrably meets many traditional sport criteria—physical demands, competitive structures, scoring systems, seasonal frameworks, and skill development through systematic training. Yet its essential artistic performance dimension and subjective evaluation components distinguish it from purely objective athletic competitions.
Perhaps the classification debate itself misses the fundamental point. Whether definitively categorized as sport, performing art, or hybrid domain, marching band participation demands extraordinary dedication, develops valuable skills, represents schools competitively, and contributes meaningfully to institutional pride and community identity. These characteristics warrant recognition commensurate with achievement significance regardless of categorical labels applied.
Schools moving beyond definitional debates toward functional equity create recognition systems celebrating excellence across all competitive domains—athletic, artistic, academic, and civic. These comprehensive approaches build inclusive school cultures where diverse student talents receive appropriate honor, where achievement recognition reflects dedication and excellence rather than traditional categorical hierarchies, and where all students see themselves reflected in institutional celebration of success.
The recognition frameworks outlined in this guide provide practical starting points for schools committed to honoring marching band excellence appropriately. Whether through expanded physical displays, comprehensive digital systems, or integrated recognition programs, these approaches ensure band students receive celebration matching their remarkable dedication, skill, and contribution to school communities.
When administrators ask “is marching band a sport?”, perhaps the better question becomes: “How can we ensure marching band achievements receive recognition reflecting their significance regardless of classification?” This reframing redirects energy from definitional debates toward practical solutions building comprehensive school pride and inclusive achievement celebration.
Students investing thousands of hours developing musical mastery while achieving peak physical fitness, executing complex choreography with mathematical precision, competing under intense pressure, and representing their schools with distinction deserve recognition honoring that complete commitment. Whether that recognition arrives through sport classification or parallel systems matters less than ensuring it arrives at all—visible, prominent, and appropriate to excellence demonstrated.
Schools ready to enhance marching band recognition can explore comprehensive digital solutions that celebrate diverse student achievements through unlimited content capacity, rich multimedia integration, and equal visibility alongside traditional athletic recognition. Request your free custom demo to discover how modern recognition displays can honor marching band excellence while building comprehensive school pride that celebrates all forms of student achievement.